|
Lucas Relic I'm currently a PhD student at ETH Zürich, advised by Markus Gross. My PhD is part of a joint program between the Computer Graphics Laboratory and Disney Research|Studios. I work on learning-based methods for data compression. I'm interested in applied research of deep learning and generative AI to domains such as data compression and computer graphics. My current research is about using generative models as a strong prior for data compression, particularly at extremely low bitrates. I previously worked in computational neuroscience, focusing on improving the quality of prosthetic vision. Earlier, I earned my B.S. and M.S. at UCSB in computer engineering and computer science, respectively. |

|
Research |
|
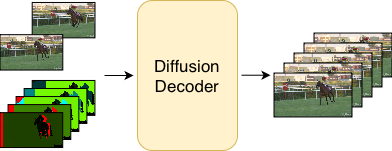
Spatiotemporal Diffusion Priors for Extreme Video Compression
Lucas Relic, André Emmenegger, Roberto Azevedo, Yang Zhang, Markus Gross, Christopher Schroers Picture Coding Symposium, 2025 (Oral Presentation) paper We built a video codec by performing long-context generative interpolation constrained by known pixel locations. |
|
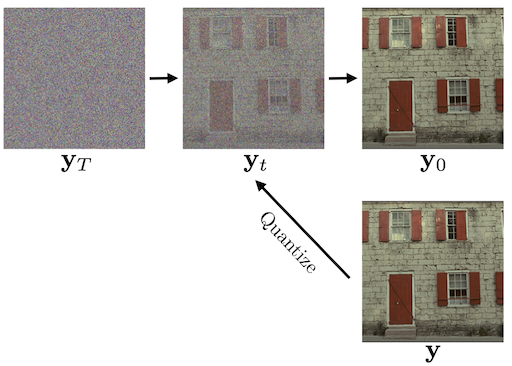
Bridging the Gap between Gaussian Diffusion Models and Universal Quantization for Image Compression
Lucas Relic, Roberto Azevedo, Yang Zhang, Markus Gross, Christopher Schroers CVPR, 2025 paper / arXiv / BibTeX initial version presented at Machine Learning and Compression Workshop @ NeurIPS, 2024 paper We developed a quanitzation-based diffusion forward process and a uniform noise diffusion model, which improves compression performance at extremely low bitrates. |

|
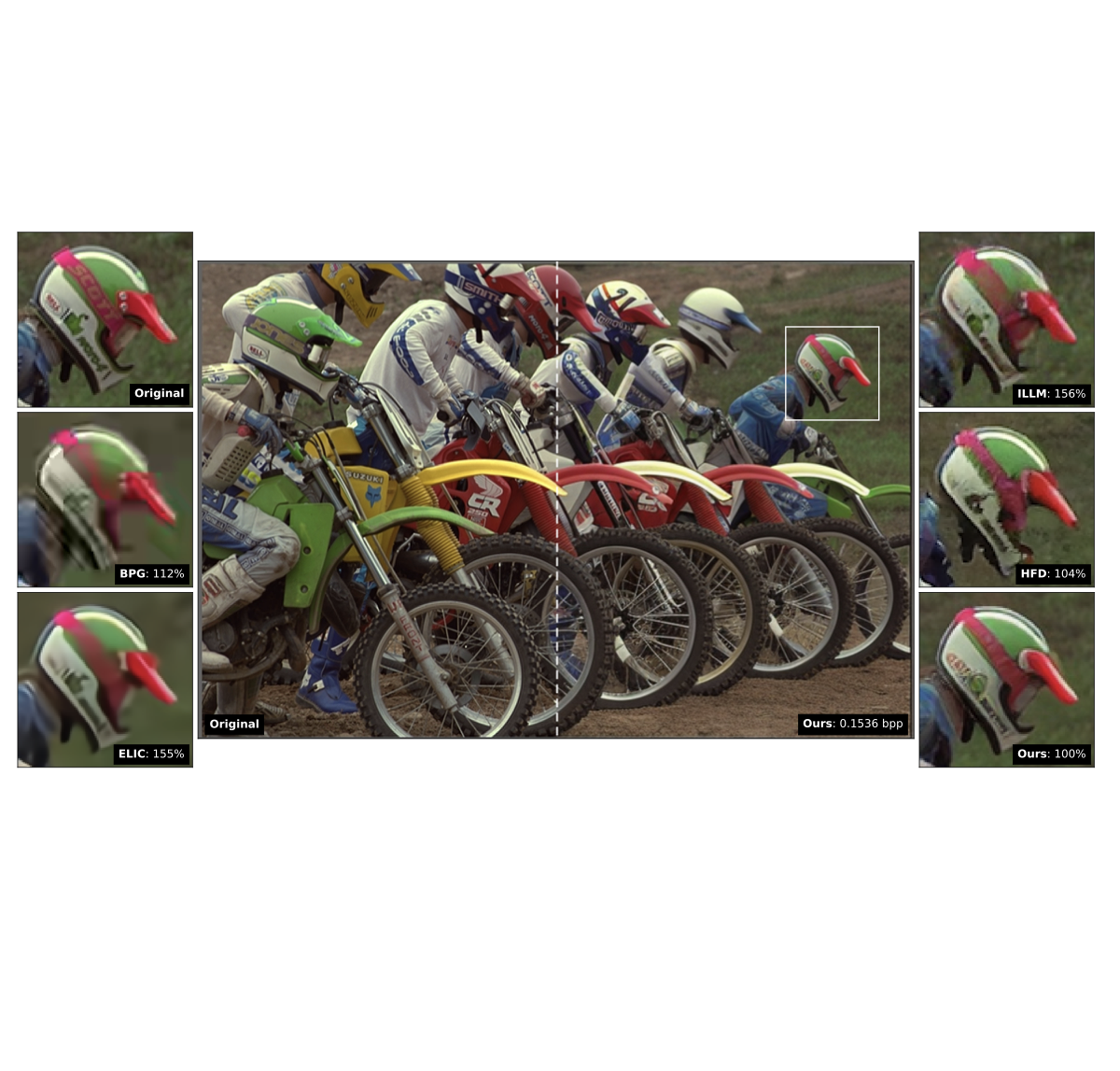
Lossy Image Compression with Foundation Diffusion Models
Lucas Relic, Roberto Azevedo, Markus Gross, Christopher Schroers ECCV, 2024 paper / arXiv / BibTeX Foundation diffusion models can be built into an image codec by using them to "undo" quantization error. |

|
Neural Video Compression with Spatio-temporal Cross-covariance Transformers
Zhenghao Chen, Lucas Relic, Roberto Azevedo, Yang Zhang, Markus Gross, Dong Xu, Luping Zhou, Christopher Schroers ACM Multimedia, 2023 paper / BibTeX We developed a novel transformer block to better capture spatio-temporal dependencies between frames in neural video compression. |
|
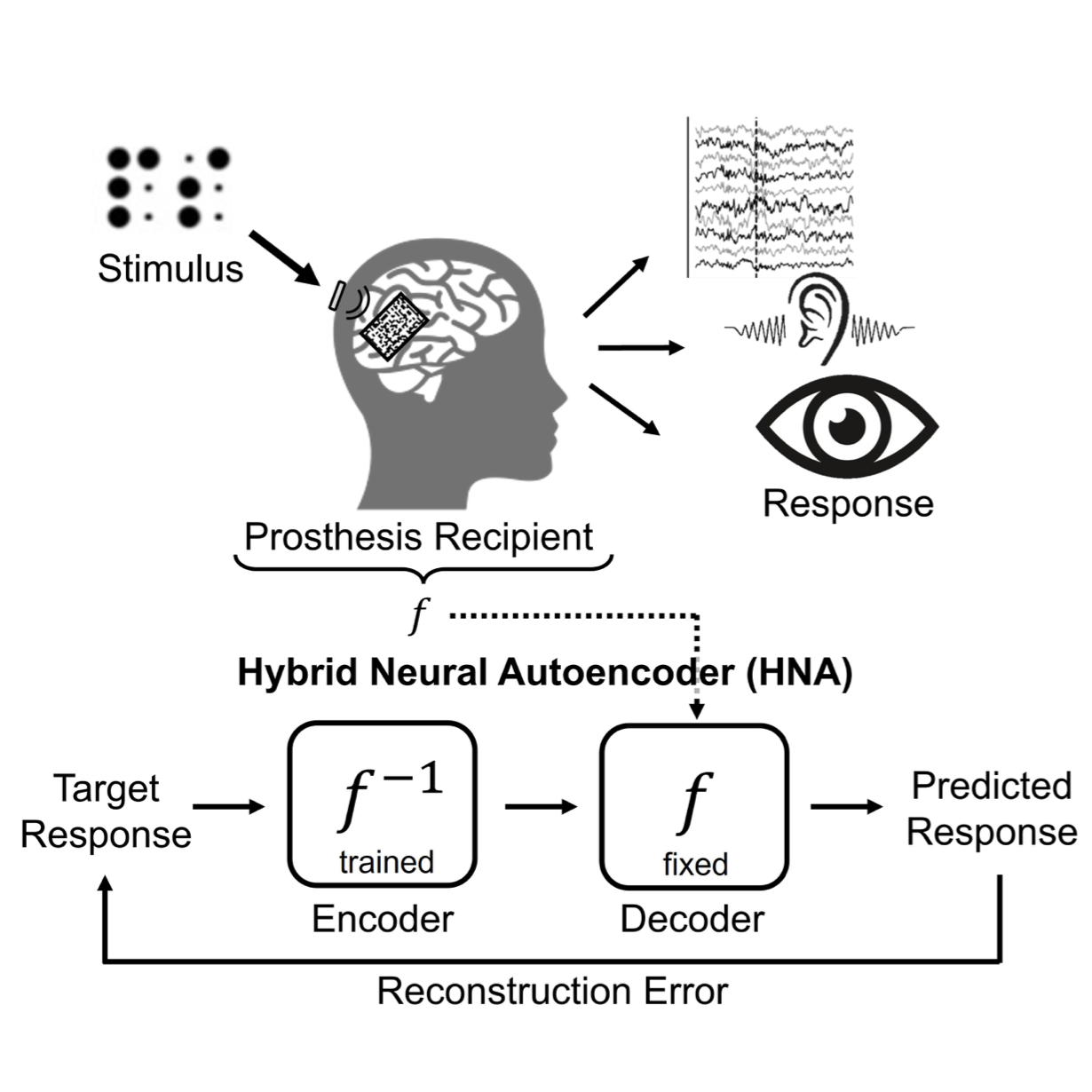
Hybrid Neural Autoencoders for Stimulus Encoding in Visual and Other Sensory Neuroprostheses
Jacob Granley, Lucas Relic, Michael Beyeler NeurIPS, 2022 paper / arXiv / BibTeX By using a differentiable model of the human retina within an autoencoder, we optimized input stimuli for retinal implants (or any neuroprosthesis with a differentiable computational model). |
|
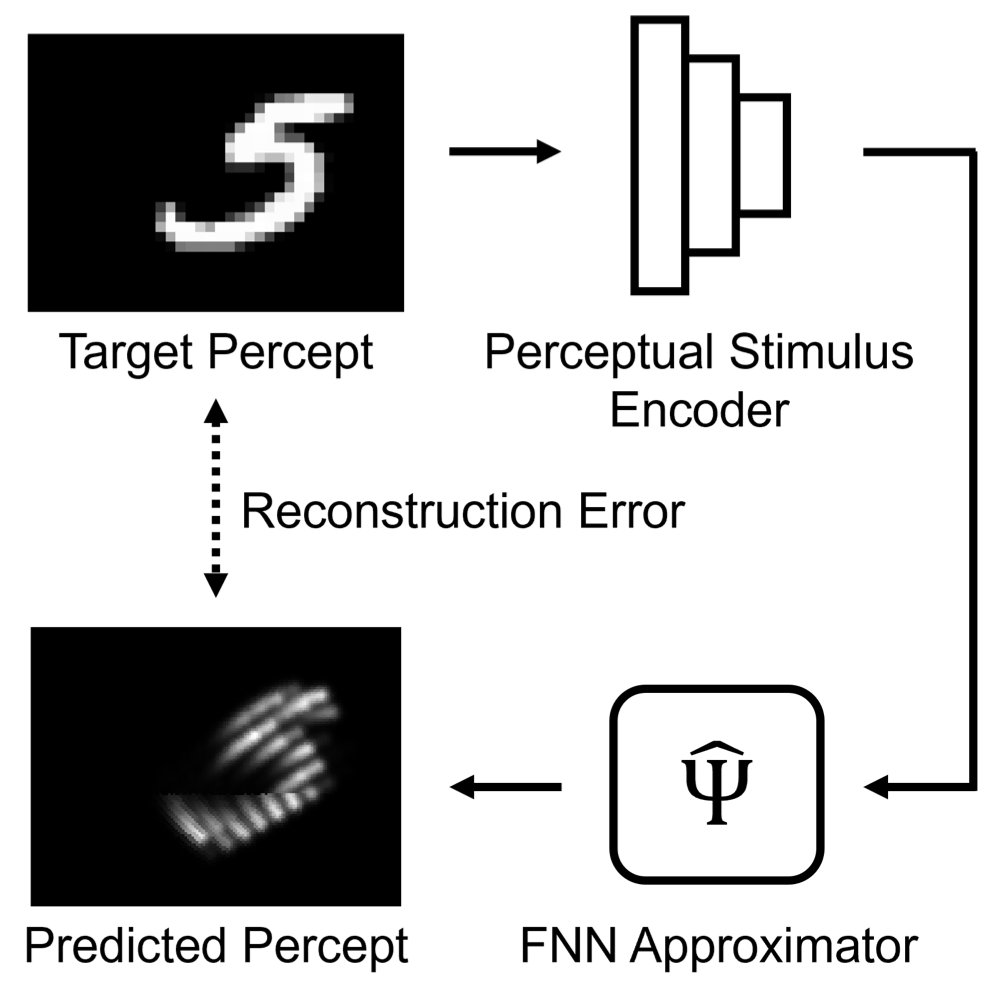
Deep Learning-Based Perceptual Stimulus Encoder for Bionic Visions
Lucas Relic, Bowen Zhang, Yi-Lin Tuan, Michael Beyeler ACM Augmented Humans, 2022 (Best Poster Award) arXiv / BibTeX We optimized the input to visual prosthetics using a neural approximation of a human retinal model. |
|
Website design from Jon Barron. |